14-12-2010
Numerical data types: The number which is not having fractional part will come under numerical data types. These are classified into two types:
1. Signed
2. Unsigned
1. Signed: Signed will allow positive value and negative values.
Signed data types are classifeid into four types
a. SByte
b. Short
c. int
d. Long
a. SByte: Here 'S' represents signed, pre-defined size of SByte is '1' byte
It can hold maximum 8 bits of signed integers.
Base type of "SByte" is "System.SByte"
b. Short: Predefined size of short is 2 byte it can hold maximum 16 bits of signed integers.
The base type of short is "System.Int16".
Data Type Size in Bytes Size in Bits CTS(Base Type)
a. SByte 1 Byte 8 bits System.SByte
b. short 2 Byte 16 bits System.Int16
c. int 4 Byte 32 bits System.Int32
d. Long 8 Byte 64 bits System.Int64
Unsigned: Unsigned will allows only positive values.
Unsingned data types are classified into 4 types.
Data Type Size in Bytes Size in Bits CTS(Base Type)(U --> represents unsigned)
a. Byte 1 Byte 8 bits System.Byte
b. ushort 2 Byte 16 bits System.UInt16
c. uint 4 Byte 32 bits System.Int32
d. ulong 8 Byte 64 bits System.Int64
Note: VB.Net will not support unsigned data types.
2. Floating point data types: The number which is having fractional part will come under floating point data types.
Eg: 10.4, 10.5, 20.5
Floating point data types will support only signed data types which will not support unsigned data types.
These are classified into 3 types.
a.Float: Predefined size of float is 4 bytes and it can hold maximum 32 bits of floating values.
The base type is system.single
b. double: Predefined size of double is 8 byte, it can hold max 64 bit of floating values.
The base type is system.double
C. decimal: Predefined size of decimal is 16 bytes, it can hold max 128 bits of floating values & the base type is system.decimal
3. Character related data types:
a. Char: Pre defined size of char is 2 byte, it can hold max 16 bit of uni-code characters & the base type of char is system.char
b. unicode characters: Computer can not understand A B C D which can understand only uni-code characters, that means every key of the keyboard is representing with some uni-code character.
When user will press 'A' it will convert into concern uni-code character which can understand by the computer.
4. Logical data types:
Bool: Predefined size of bool is 1 bit, it can hold either true value or false value.
True is representing with '1' & false is representing with ' 0 '.
The base type of bool is system.Boolean
5. General data types:
General data types will not have the predefined sizes.
General data types are classified into 2 types.
a. String: String is representing collection of characters.
The base type of string is system.string
Ex: String s = "Sathya";
b. Object: Object is a instance of a class for all the objects base type is system. object
Eg: For float data type:
Void main()
{
float a = 4.5;
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.Read();
}
Output: Error, Because in C#.Net by default CLR will treat floating value as double data type, if we want to declare it as float data type we should post fix with ' f ' or ' F ' like below:
Void main()
{
float a = 4.5f;
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.Read();
}
Output: 4.5
Eg: For decimal:
Void main()
{
decimal a = 4.5;
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.Read();
}
Output: Error, Because if we want to declare it as floating value as decimal then we should post fix with ' m ' or ' M ' like below:
Void main()
{
decimal a = 4.5m;
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.Read();
}
Output: 4.5
Value types & Reference types:
According to data storage locations the data types are classifed into 2 types:
1. Value Types
2. Reference Types
1. Value Types: In value types the data is storing into stack memory due to that reason which can be called as stack based data types.
In value types variable contains the actual data.
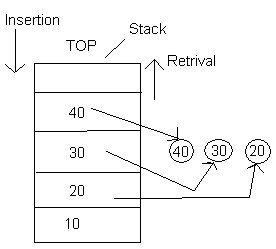
Stack: Stack is a dta structure which can contain collection of elements.
Stack data structure will supporrt only one end that is top end, that means if we want to perform insert operation or retrive operation we can perform from only top end.
Stack is following an approach called LIFO(Last In First Out), that means the last inserted element we can retrive first.